Chubu Electric Power and Toyota to Launch Electrified Vehicle Battery Reuse and Recycling Verification Project
Chubu Electric Power and Toyota Motor Corporation have concluded a basic agreement to launch a verification project for building a large-capacity storage system that reuses batteries from electrified vehicles, and for examining how used batteries can be recycled.
Chubu Electric Power recognises the importance of accurately managing fluctuations in its energy supply-and-demand balance, caused by the recent large-scale introduction of renewable energy, and is promoting efforts to further improve operation of its electric power system.
Toyota is actively promoting the use of electrified vehicles (as expressed in the Toyota Challenge to Promote Widespread Use of Electrified Vehicles, published in December 2017) and looking at how the effective use of batteries and development of social infrastructure can support that goal.
Battery reuse
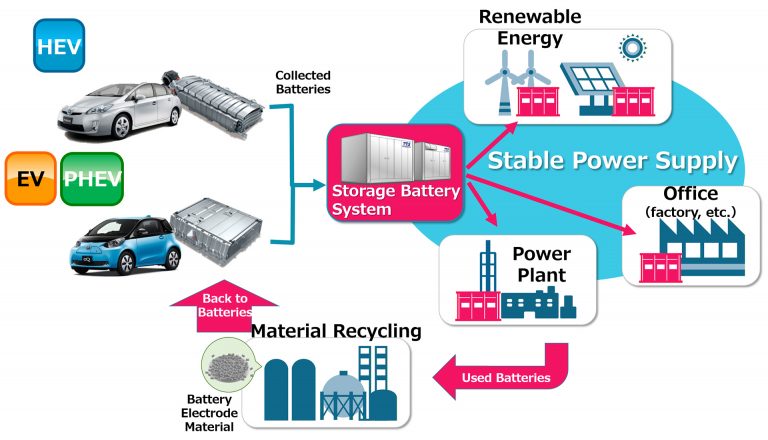
Under the new agreement, the two companies aim to reuse batteries collected from Toyota electrified vehicles as a storage system to meet different challenges in the electric power system.
When combined in large numbers, used batteries, even with reduced performance levels, can be repurposed to handle adjustments in energy supply and demand, and to manage frequency and voltage fluctuations in power distribution systems. These are all issues that accompany the widespread introduction of renewable energy.
Not only can these efforts serve as a solution to challenges within the electric power system, Chubu Electric Power and Toyota expect them to have positive effects in the operation of thermal power plants.
1. Utilisation for energy supply-demand adjustment
2) Utilisation to counter frequency fluctuations
3. Utilisation to counter voltage fluctuations in distribution systems
During the 2018 financial year, Chubu Electric Power and Toyota will start verification of the Storage Battery System. Based on the results of this test, the two companies aim to introduce a power generation capacity of 10,000kW – equivalent to 10,000 batteries – in the 2020 financial year.
The initial stage will involve nickel-metal hydride batteries, currently being used in large quantities, mainly in hybrid electric vehicles. By around 2030, the plan is to also include lithium-ion batteries from battery electric and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles.
Battery recycling
The two companies will consider establishing a mechanism to recycle reused batteries, collecting materials such as rare-earth metals, and reusing them.
Both companies will continue to contribute to the further development of the region, aiming to achieve a resource recycling, low-carbon society through initiatives such as the commercialisation of battery reuse and recycling.