Toyota unveils new technology that will change the future of cars
- Technology to pioneer the future, centring on innovative battery EV technology and the establishment of a hydrogen business
Under the banner “let’s change the future of cars,” Toyota Motor Corporation (Toyota) has announced a range of a new technologies that will support its transformation into a mobility company.
At a technical briefing in Japan, Hiroki Nakajima, Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer, explained Toyota’s technology strategy and the future direction of car manufacturing. He also talked about specific and diverse technologies, including concepts currently under development, that will help Toyota achieve the vision and policies it has communicated.
He was joined by Takero Kato, president of Toyota’s new BEV production centre, and Mitsumasa Yamagata, who is scheduled to become president of the company’s hydrogen factory, to be launched in July. They provided more detail on their respective strategies for the battery EV and hydrogen businesses.
PRESENTATIONS
Toyota’s technology and car manufacturing direction, Hiroki Nakajima, Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer
Toyota gave an explanation of the Toyota Mobility Concept at its public briefing in April. The three approaches key to its realisation are electrification, intelligence and diversification.
In the area of electrification, we will continue to pursue a “multi-pathway approach,” including the introduction of optimal powertrains for each region.
In the area of intelligence, in addition to vehicles and services, we will also promote initiatives to expand our connection with society, such as Woven City.
We will also continue to diversify our business by expanding our scope from “cars” to “society,” to include freedom of mobility and diverse energy options for all.
To promote these three themes technologically, we have been shifting resources to Advanced Development fields and actively investing in future-oriented areas since 2016, when the company system was inaugurated.
As of March 2023, we have shifted more than half our R&D staff and approximately half of our R&D expenses to Advanced Development fields, while increasing the total amount. We will accelerate this trend in the future.
We would like to promote car manufacturing based on three axes. The first is to pursue safety and security without compromise. We will further refine Toyota Safety Sense and deliver safe and reliable technologies to our customers.
The second is that the future will be built by everyone. We will create the future by connecting with our colleagues around the world through initiatives such as CJPT’s (Commercial Japan Partnership Technologies Corporation) efforts to decarbonise the commercia sector; our partnership with the CP Group in Thailand; and our collaboration in motorsports.
Third, we will accelerate localisation. As the needs of our customers in each region will differ further in the future, we will accelerate “development near our customers” at our R&D bases around the world.
Toyota has overcome what were considered to be difficult challenges with its technological capabilities and has developed numerous vehicles that are ahead of the times and paving the way for the future, such as Prius – now synonymous with hybrid vehicles – and the Mirai fuel cell car.
Let’s change the future of cars. We will continue to lead in creating a future society by using the power of technology to transport our customers into the future and connecting cars to society.
Next generation battery EV strategy, Takero Kato, BEV Factory President
What we hope to achieve with the BEV Factory – an organisation dedicated to battery EVS, launched in May – is to change the future with BEVs through the transformation of cars, manufacturing and the way we work.
On the vehicle axis, through technologies such as the integration of next generation batteries and sonic technology, we will achieve a vehicle cruising range of 1,000km. To produce more stylish designs, AI will be used to support aerodynamic performance, while designers will focus on expressing natural sensibilities. The Arene OS and full OTA (over-the-air) application will infinitely expand the possibilities for how cars can be enjoyed. Like the EV with a manual transmission, we will deliver exciting surprises and fun to our customers, with technologies that can only be achieved by a carmaker.
On the manufacturing axis, car bodies will be constructed from three main components in a new modular structure. Adopting giga casting will allow significant component introduction, which in turn will contribute to the reduction of vehicle development costs and factory investment. In addition, self-propelling production technology will reduce process and plant investment by half.
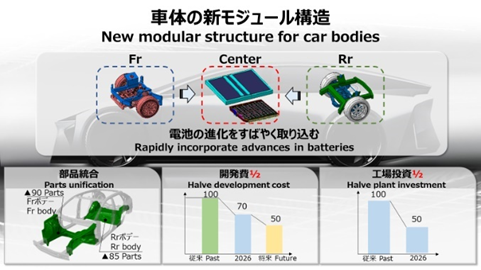
The BEV Factory is an “ALL IN ONE TEAM,” under a single leader, unifying functions and regions beyond the framework of carmaker, including Woven by Toyota and external partners.
This ONE TEAM will revolutionise the way we work, with everyone on the same site and with the same awareness of the issues, achieving quick initial response and decision making.
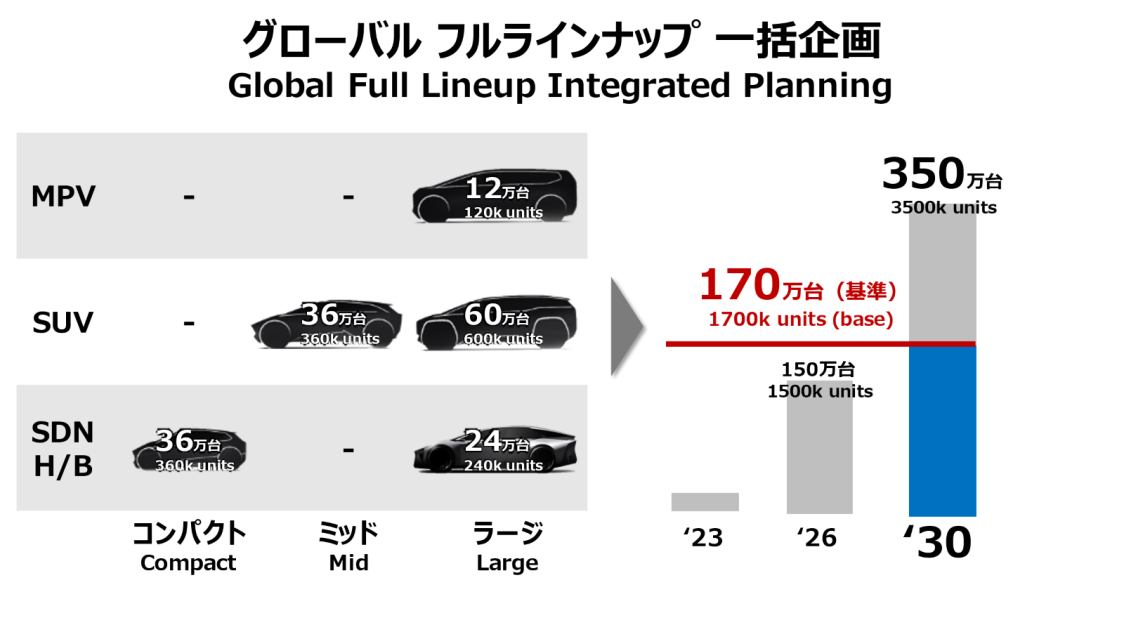
We will roll out next generation BEVs globally and as a full line-up to be launched in 2026. By 2030, 1.7 million units out of 3.5 million overall will be provided by the BEV Factory. These next generation BEVs will adopt new batteries, with which we are determined to become a world leader in BEV energy consumption. With the resources we earn, we will improve the appeal of our products to exceed customer expectations and secure earnings.
Hydrogen business strategy, Mistumasa Yamagata, Hydrogen Factory President-designate
The hydrogen markets in Europe, China and North America will be the world’s largest by 2030. The fuel cell market is expected to expand rapidly towards that point, reaching the value of 5 trillion yen (approximately £5.7 billion) per year. We are promoting external sales of fuel cells, using the Mirai’s hydrogen units; we have received offers for 100,000 unit sales by 2030, most of them for commercial vehicles.
To respond to the rapid changes in the market, we will establish a new organisation, the Hydrogen Factory, in July this year. This will be able to make immediate decisions under one leader, from sales to development and production, all at once.
The Hydrogen Factory will promote business on three axes. The first is the localisation of R&D and production in countries within the major world markets. We will accelerate our efforts by establishing local bases, mainly in Europe and China.
The second is the strengthening of alliances with leading partners. We will do our best to deliver affordable fuel cells to our customers by consolidating sufficient quantities through alliances.
The third is competitiveness and technology. We will work on the “innovative evolution of competitive next generation FC technologies,” such as cell technologies and FC systems.
We will work towards full-scale commercialisation as we move forward with these initiatives. The next generation system will achieve a 37 per cent cost reduction through technological progress, volume efficiency and localisation. Furthermore, in collaboration with partners, if we receive and offer for 200,000 units in 2030, we will be able to reduce the cost by 50 per cent and generate a solid profit, while meeting the expectations of our customers and governments.
We will work together in development production and sales to achieve this goal.
The price of hydrogen remains very high. To promote the widespread use of hydrogen, Toyota will continue to work with its partners to contribute to the production, transportation and usage of hydrogen.
We will take the relationships we have built with strong partners as opportunities to commercialise hydrogen by establishing customer-oriented bases in major markets and by offering affordable products in sufficient quantities.
BATTERY TECHNOLOGIES
Batteries: innovation supporting Toyota’s evolution of next generation BEVs
The battery is the heart of a BEV. Just as the heart pumps blood through the body, the battery feeds electricity to the vehicle.
As Toyota advances its effort towards introducing next generation BEVs in 2026, it is also evolving batteries with new technologies to meet customer expectations.
Liquid lithium-ion batteries, which are currently the mainstream, will gain enhanced performance through improvement of energy density in square batteries, an area where Toyota has long expertise. In addition, by adopting the bipolar structure that has been developed for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) to BEVs, we will expand our line-up and provide customers with a range of options, from low-cost popular batteries to ones designed for higher performance.
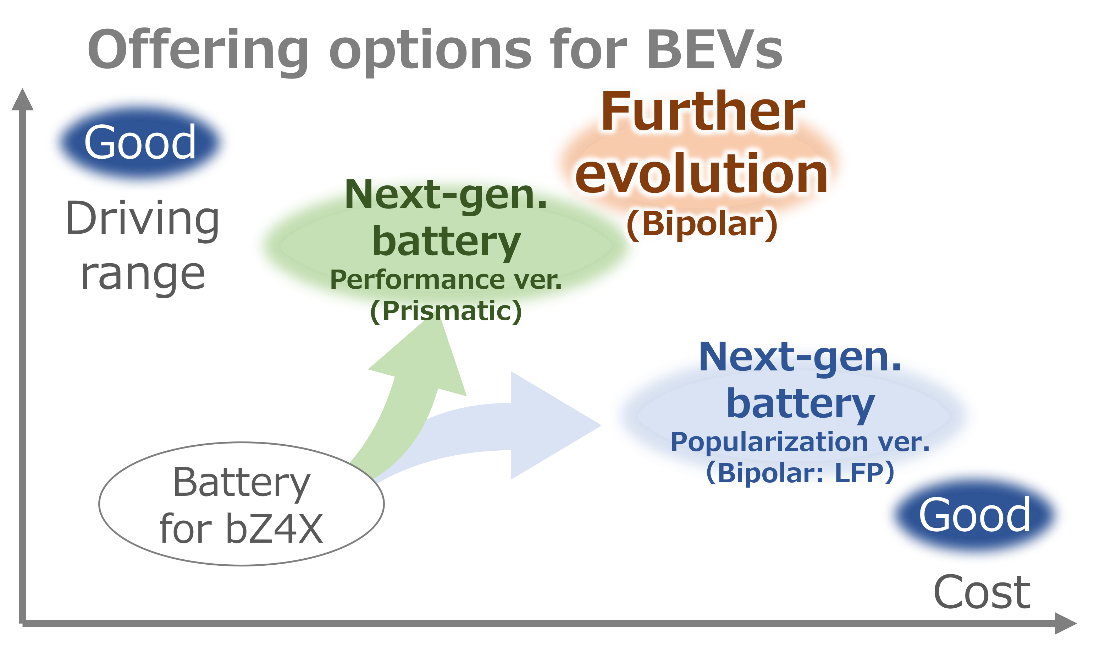
Furthermore, highly anticipated all-solid-state batteries are entering the practical application phase for use in BEVs. Toyota’s full line-up of competitive batteries will support the future evolution of the company’s BEVs.
Note: The performance version of the next generation battery is being developed with Prime Planet Energy and Solutions Corporation; the popular and high-performance versions of the next generation batteries and all-solid-state battery for BEVs are being developed with Toyota Industries Corporation, combining the knowledge within the Toyota Group.
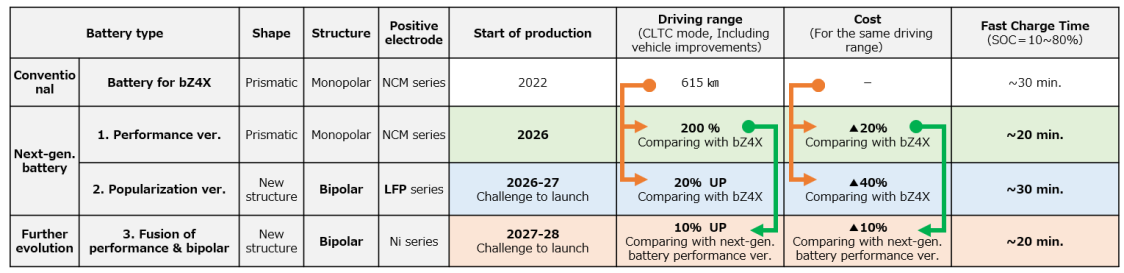
Next generation batteries: performance version
- The next generation BEV, to be introduced in 2026, will have a cruising range of 1,000km (approx. 620 miles)1. Toyota is developing a square battery with a focus on performance for installation in such cars.
- While the battery’s energy density will be increased, the cruising range will be increased through higher efficiency, in areas such as aerodynamics and weight reduction. At the same time, costs will be reduced by 20 per cent compared to the current bZ4X, and quick charging (SOC 10-80 per cent) will take 20 minutes or less.

- Toyota is also developing good, low-cost batteries that will contribute to the spread and expansion of BEVs, providing customers with a variety of battery choices.
- The bipolar structure battery, which has been used in the (Japan market) Aqua and Crown hybrid vehicles, is now being applied to BEVs. This uses inexpensive lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and is expected to be put to practical use in 2026-2027.
- Toyota is aiming for a 20 per cent increase in cruising range, a 40 per cent reduction in cost and quick recharging in 30 minutes or less (SOC 10-80 per cent) compared to the current bZ4X. It is considering installing the battery in BEVs in the popular market price range.
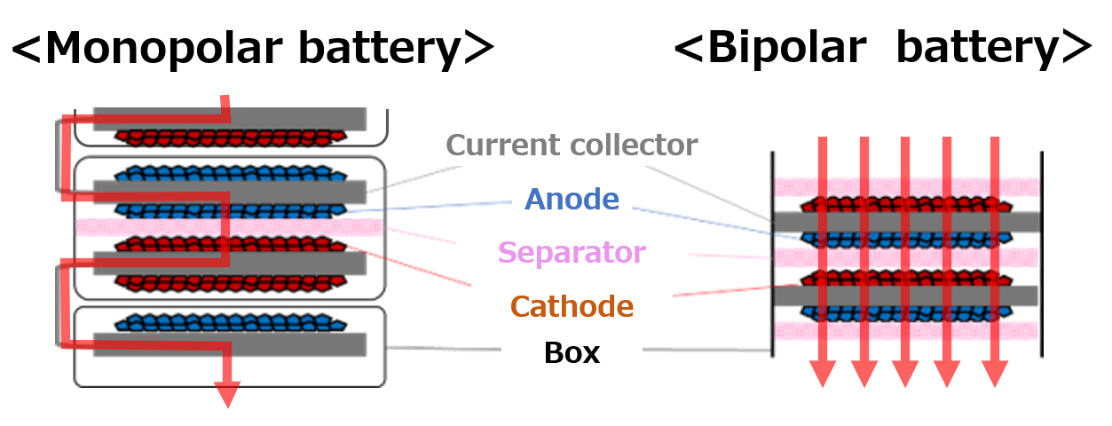
Bipolar lithium-ion battery: high-performance version
- In parallel with development of the “popular” battery version, a high-performance battery that combines a bipolar structure with a high nickel cathode to achieve further advances will be put to practical use in 2027-2028.
- It will achieve even greater performances than the “performance” version of the square battery with a 10 per cent increase in cruising range, a 10 per cent reduction in cost and a quick charge time of 20 minutes or less (SOC 10-80 per cent).
All-solid-state batteries for BEVs
- Having discovered a technological breakthrough that overcomes the longstanding challenge of battery durability, Toyota is reviewing the introduction of all-solid-state batteries for conventional HEVs and accelerating their development as a battery for BEVs, for which expectations are rising.
- Toyota is currently developing a method for mass production, striving for commercialisation in 2027-2028.
- Toyota is looking at a 20 per cent improvement in cruising range, compared to the “performance” version of the square battery. Costs are under scrutiny and the aim is for a quick charging time of 10 minutes or less (SOC 10-80 per cent). With an eye to the future, a higher-level specification is being researched and developed at the same time, with the aim of a 50 per cent improvement in cruising range, compared to the “performance” version of the square battery.

1Including vehicle efficiency improvements, in areas such as aerodynamics and weight reduction.
AERODYNAMICS
Toyota is studying the application of hypersonic technology used in rockets to BEVs. It is collaborating with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries on a new technology that can reduce aerodynamic drag in any shape.
In addition to battery innovation, Toyota will take on the challenge of further extending cruising range by minimising aerodynamic drag, improving BEV performance beyond customer expectations.
Aerodynamic technology based on hypersonic rocket technology
- Toyota is studying the technology in cooperation with the Space Systems Division of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
- It is aiming to introduce its findings as fundamental technologies for next generation BEVs.
- By being able to reduce aerodynamic drag without being restricted by the shape of the car, it is expected to combine an attractive design and packaging with aerodynamic performance (Cd0.1 level in view).
- Technology development is under way in different speed ranges, applying knowledge of boundary layer control in the ultra-high-speed range obtained from aerospace technology.
PRODUCTION PROCESSES
To ensure the profitability of BEVs, Toyota will work on both vehicle technology and manufacturing methods.
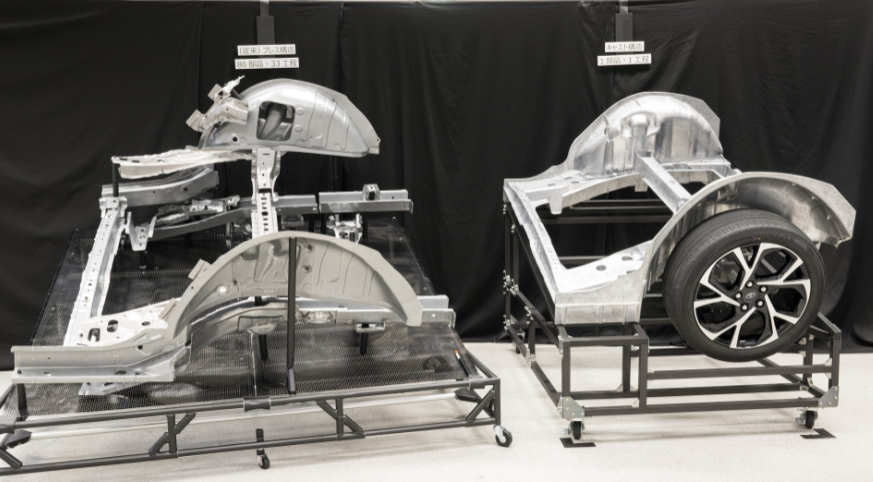
First, the vehicle body will have a simple and slim structure, moulded using giga casting, for significant parts integration.
Also, Toyota will create highly flexible production plants without conveyors, introducing concepts such as a self-propelling assembly line.
Digital technology will be used in the design of the BEV production plant, to increase the accuracy of process verification. Through these efforts, Toyota aims to reduce the production preparation lead time, production process and factor investment for mass-production.
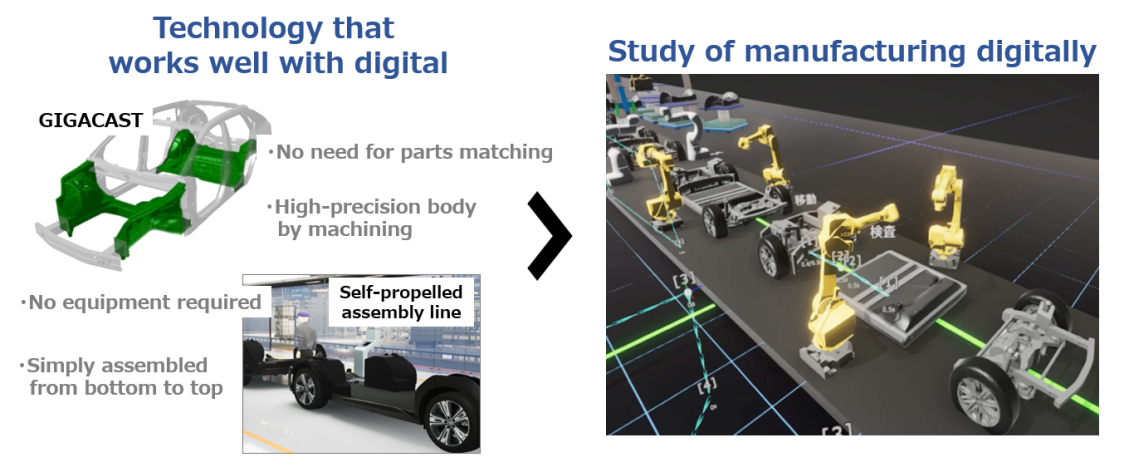
Giga casting
- This process achieves high productivity, with integrated moulding of optimum shapes.
- Toyota is also developing technology for integrated moulding with aluminium die casting, for what previously was made with dozens of sheet metal parts.
- After analysing car manufacturing casting technology that has achieved a high degree of precision, Toyota has reviewed the structural design to make it simpler and slimmer.
- As well as reducing the number of parts and processes, it also reflects the Toyota Production System (TPS) philosophy of eliminating waste in each process.

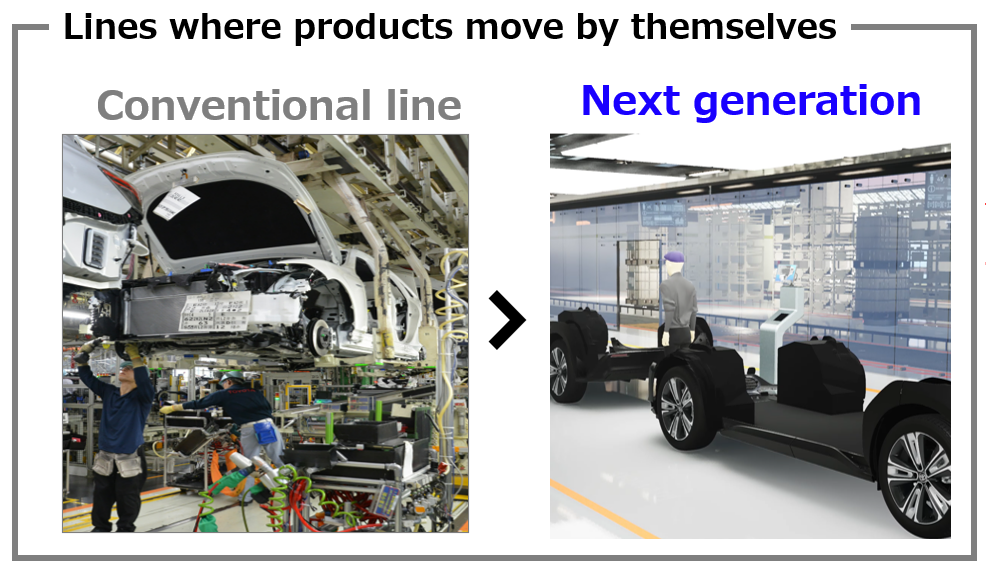
Self-propelling assembly line
- Toyota will take on the challenge of designing a next generation production plant that dispenses with the concept of a conveyor.
- This technology is being developed so that mass-produced cars under assembly can move from one process to the next on their own.
- Sensors and control systems on the factory side communicate with wireless terminals on the vehicles to control them externally. Toyota thus aims to integrate the car and the production plant.
- Eliminating conveyors will make factory layouts more flexible and significantly reduce factory investment, lead times and the human resources required to prepare for mass production – activities that used to take years.
Next generation production plant design
- Toyota will look at digital technology for manufacturing in its next generation BEV plant.
- Technologies such as giga casting and self-driving assembly lines are compatible with digitisation; digital technology will be actively employed, including for process study and improvement.
- Lead-time preparation for mass production will be reduced through reproduction accuracy to 1mm error level.
- Toyota will shift to more efficient production lines with unmanned transport, using methods such as connected technology, autonomous inspections and others. It will take up the challenge to drastically change manufacturing, by adopting TPS concepts and other measures.
FUNDAMENTAL TECHNOLOGIES TO IMPROVE BEV PRODUCT APPEAL
Toyota is further developing fundamental technologies, making the most of those it has cultivated through manufacturing. The Toyota Group as a whole will take advantage of the small eAxle and next generation semiconductor technologies to improve the commercial potential of BEVs under development.
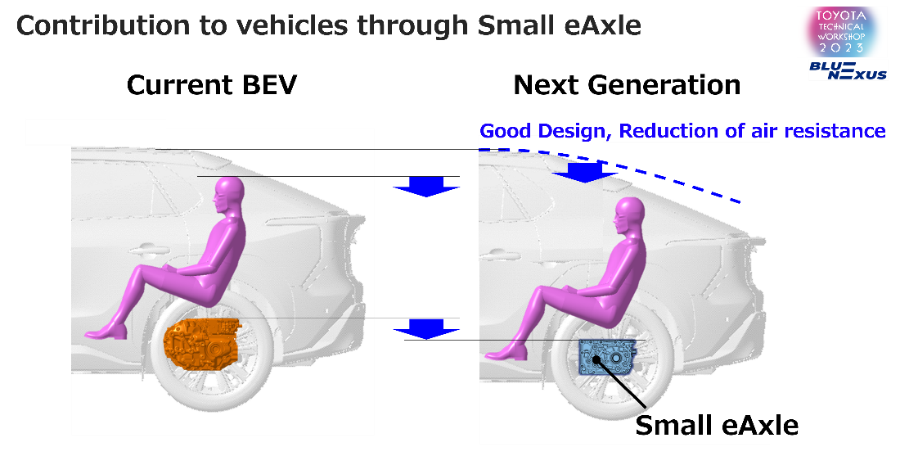
Small eAxle
- Toyota is developing a small eAxle, downsizing key components such as the motor, geartrain and inverter. It is making full use of BlueE Nexus, Aisin, Denso and its own in-house technologies, cultivated through the development of HEVs.
- By downsizing the eAxle, a longer cruising range has been realised. The smaller unit also increases the vehicle’s load space and reduces aerodynamic drag, contributing to better comfort and design.
SiC wafers for BEV inverters
- Next generation semiconductors with 50 per cent less power loss.
- Development of semiconductor materials from crystal growth will contribute to improvement in BEV energy consumption.
- In addition to the gas method, which has the advantage of 10 times faster crystal growth than the industry standard, Toyota is developing the industry’s largest eight-inch wafer. This will promote the internalisation of technology within the Toyota Group.
MULTI-PATHWAY PLATFORM
Toyota has the technological capability to deliver BEV models immediately through a multi-pathway platform for a variety of electrified vehicles. It will expand its product line-up even before the introduction of next generation BEVs, with standard set for 1.5 million units in 2026.
Multi-pathway platform
- Toyota will develop a platform that will enable it to offer a variety of electrified vehicles.
- As an example of its capability to provide not only the bZ model range, but also fun-to-drive BEVs to meet the diverse needs of customers, it has converted the powertrain of the (Japanese market) Crown model into a BEV.
HYDROGEN
Toyota positions hydrogen an important fuel in its efforts to reduce CO2 emissions and achieve the aim of carbon neutrality. To help create a “hydrogen society” by promoting the use of hydrogen, it is working with industry partners in areas of hydrogen production, transportation and usage.
It is also developing and demonstrating fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), including passenger cars, commercial trucks and buses, FC stationary generators and vehicles using hydrogen combustion engines.
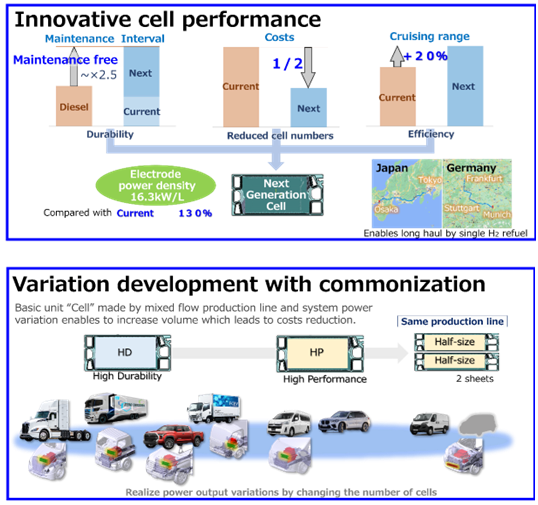
Next generation FC system
- Toyota is developing innovative, next generation fuel cells that will deliver industry-leading performance for commercial use, with long life, low cost and low fuel consumption. It aims for these to be commercialised in 2026.
- It is pursuing easier maintenance requirements compared to diesel-engine vehicles and to reduce the cost of a fuel cell stack by half, compared to current models. It also expects to improve the cruising range by 20 per cent, compared to today’s system.
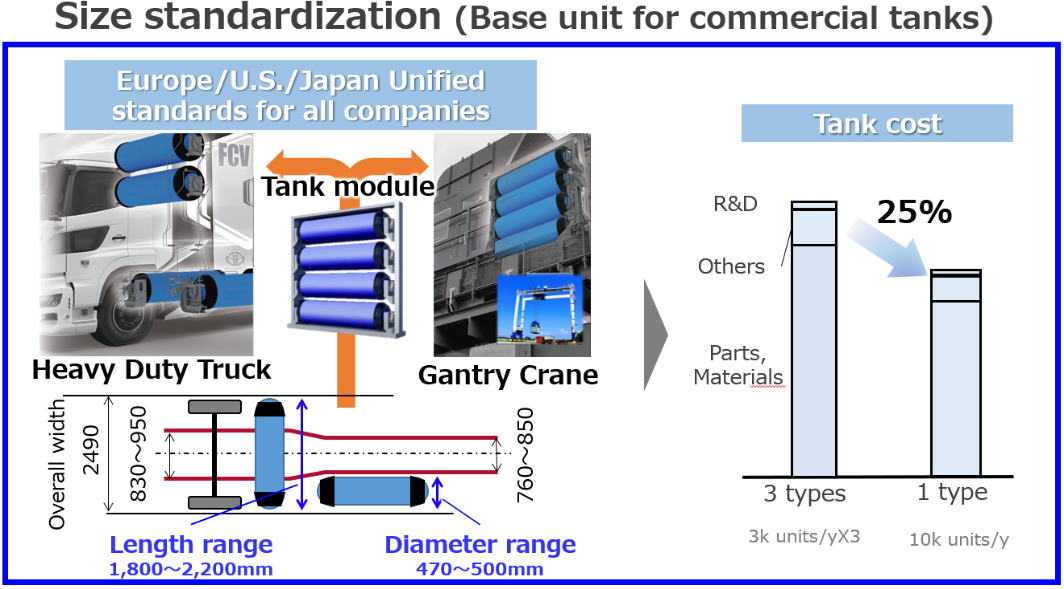
Large commercial tanks
- Toyota is taking on the issue of standardising tanks for large commercial vehicles, which are expected to consume large volumes of hydrogen. This will help accelerate hydrogen demand. The aim is to reduce manufacturing costs by 25 per cent by unifying the tank standards for European, American and Japanese companies and consolidating their quantities.
- Toyota is also developing liquid hydrogen tanks for large commercial vehicles.
Multi Hydrogen Tank concept
- Toyota is developing hydrogen tanks that are easy to install and compatible with different vehicle types and sizes. It will be possible to convert existing vehicles to use hydrogen fuel cells and hydrogen combustion engines.
Hydrogen production – by water production or from biogas
- Toyota has produced a new water electrolyser to produce hydrogen, applying the fuel cell stack and cell technologies it developed for the Mirai FCEV. Public trials of the unit have started at Denso’s Fukushima plant.
- Toyota has launched an initiative to produce hydrogen from biogas derived from local chicken manure and food waste in Thailand by the end of 2023, working in collaboration with Mitsubishi Kakoki Corporation and Toyota Tsusho Corporation.
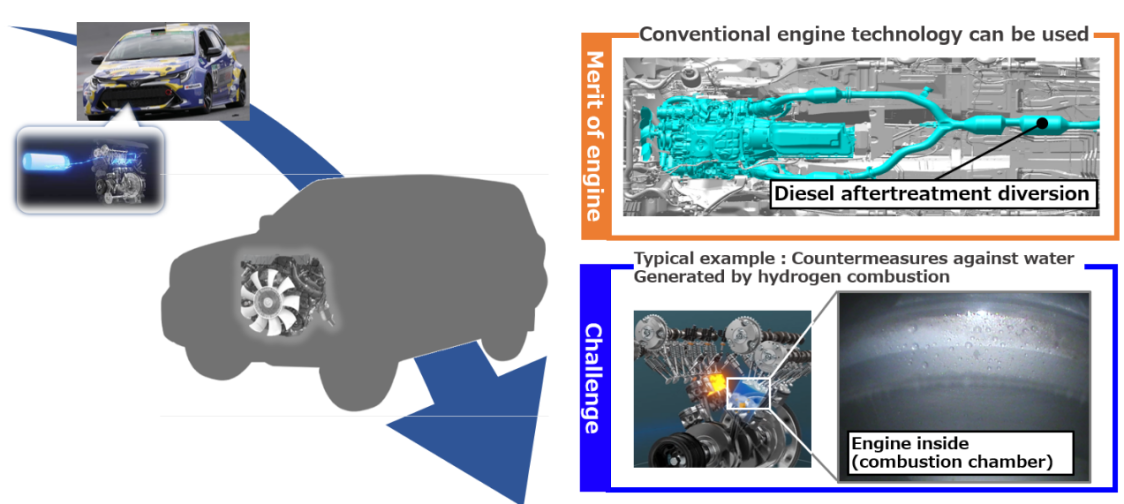
Hydrogen-engine vehicle
- Toyota has developed a trial hydrogen-engine vehicle, licensed to be driven on public roads in Japan.
- It will accelerate the development of hydrogen-engine vehicles for commercialisation, as new option for contributing to carbon neutrality.
- It will promote consideration of the entire vehicle, for example incorporating an exhaust purification system that uses established diesel engine technology.
CARBON-NEUTRAL (CN) FUEL
Toyota will work with various partners to promote the use of biofuels, which will lead to CN fuel for customer-owned vehicles.
To achieve carbon neutrality, it is important not only to promote the spread of electrified vehicles, especially new car sales, but also to reduce CO2 emissions from cars that are already on the road and being used daily by customers.
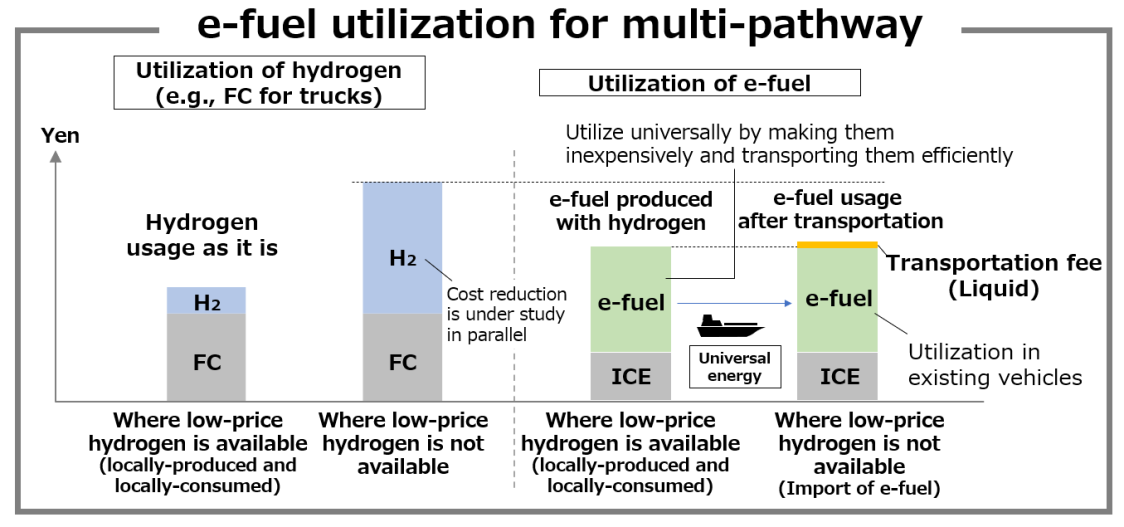
To meet the requirements of diverse vehicle types, regions and customers, a variety of energy options must be offered. Toyota is working with various partners, across industry boundaries, to reduce CO2 emissions and run public trials of hydrogen and synthetic and bioethanol fuels, based on electricity from renewable energy sources.
e-fuel
- In regions where hydrogen is inexpensive, it is produced and consumed locally as-is in fuel cell systems. In areas where hydrogen is expensive, Toyota will look the potential for realising total cost advantages by producing and transporting e-fuel.
Biofuels
- In July 2022, seven private companies, including Toyota, established the Research Association of Biomass Innovation for Next Generation Automobile Fuels to promote research of a production technology structure for second generation bioethanol fuel.
- Toyota is expanding bioethanol use in emerging countries by promoting deployment of “the right vehicle, in the right place, at the right time.” This includes the introduction of biofuel/ethanol-compatible models.
- For example, 10 per cent biofuel can be used in all vehicle types; in Brazil, Toyota HEVs are 100 per cent biofuel-compatible; and in India HEVs that can be adapted to use biofuel are to be launched (announced November 2022).
INTELLIGENCE IN CARS – ADDING NEW VALUE TO VEHICLES
Toyota will sequentially expand the updating of advanced safety technologies, multimedia and other functions to all vehicles. With a next generation voice recognition system, Arene will accelerate the shift to car intelligence, with quick response and flexible suggestions that will make the driver feel as though they are talking to a human being.
Alongside the evolution of the car’s operating system, the next generation BEV will also enable customisation of the driving “feel,” focusing on acceleration, turning and stopping. In addition, by refining the vehicle’s fundamental characteristics with hardware and software, more fun-to-drive models can be delivered.
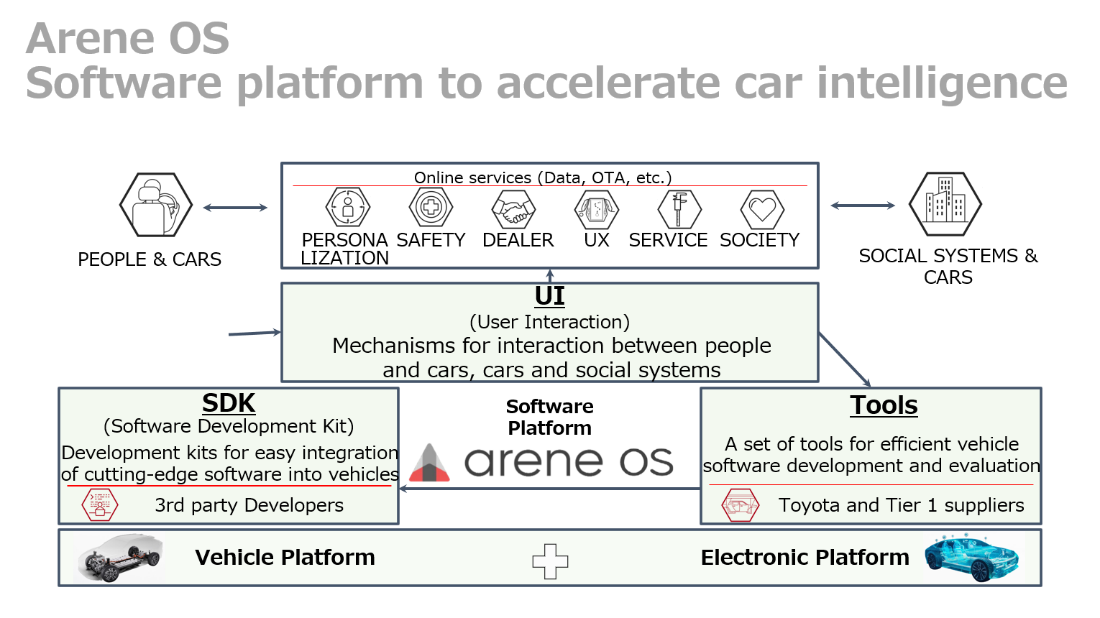
Arene OS
Arene OS is a state-of-the-art software platform that is accelerating the intelligence of cars and providing new value to customers on three pillars.
- Tools: a set of tools for efficient development and evaluation of vehicle software
- Software Development Kit (SDK): a development kit for easy integration of state-of-the-art software into vehicles.
- User Interaction (UI): mechanisms for interaction between people and cars and between cars and society.
Next generation voice recognition
- The most advanced AI technology supports a comfortable experience for customers with fast, high-performance response times and suggestions tailored to their situations and preferences, as if they were talking to a concierge.
- Arene OS operates more than 200 vehicle functions, accelerating the pace of vehicle intelligence.
- The system is scheduled for installation in Toyota’s next global volume production model.
AI-supported “stylish design”
- This tool aims to limitlessly expand the power of design ideas through collaboration between human designers and AI systems. At the same time, it can drastically improve the speed of design development.
- An AI system generates images that take aerodynamic and other engineering constraints into account in the creation of designs.
Manual transmission BEVs
- BEV hardware and software that can be updated in a way that only a carmaker can provide.
- Drive control and clutch functions provide the fun of driving a car with a manual transmission.
On-demand modifications to achieve different driving experiences
- Driving feel, engine sound and other qualities can be changed by updating the BEV software.
- Unlimited possibilities can be explored, such as recreating the feel of cars the owner used to drive, sports cars, or the imagined cars of the future.
Lexus RX with steer-by-wire
- This system controls the steering with electric signals, creating a new driving experience by significantly reducing the amount of steering input the driver has to make, compared using a conventional system with a circular steering wheel.
- With no mechanical linkage in the system and greater flexibility in in its arrangement, there is freedom to expand it to new mobility applications.
INTELLIGENCE THAT CONNECTS WITH SOCIETY AND CONTRIBUTES TO SOLVING SOCIAL ISSUES
Cars will be connected to infrastructure and towns to provide new services. For example, Toyota will promote the social implementation of logistics systems that use real-time information to improve the efficiency of transportation systems and achieve optimum energy management.
Woven City, serving as a test course for mobility, will conduct demonstrations that connect people, vehicles and society. For example, connected services will be used in public logistics to improve issues identified by the work in Woven City. By advancing this cycle, Toyota will accelerate the intelligence of society.
Safety is a top priority. Toyota is developing autonomous driving technology, using its long-accumulated safety knowledge and large amounts of data. For example, in automatic parking, the system not only traces a pre-recorded roue, it also deals with irregular situations when obstacles are encountered. Toyota’s development includes an autonomous, multi-purpose e-Palette vehicle.
The company will continue to advance intelligence and aim for “zero traffic accidents,” “freedom of movement for all” and “provision of new value in mobility”.
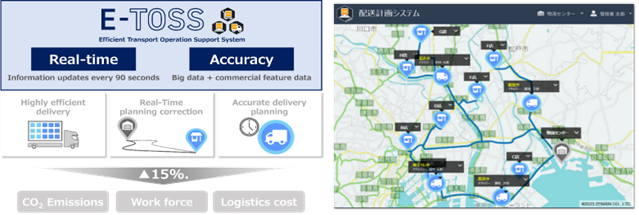
Highly Efficient Transportation Operation Support System (E-TOSS)
- E-TOSS uses vehicle data and connected technology for a real-time transportation and delivery system.
- It provides accurate planning that contributes to reductions in CO2 emissions, manpower and logistics costs, the latter by around 15 per cent.
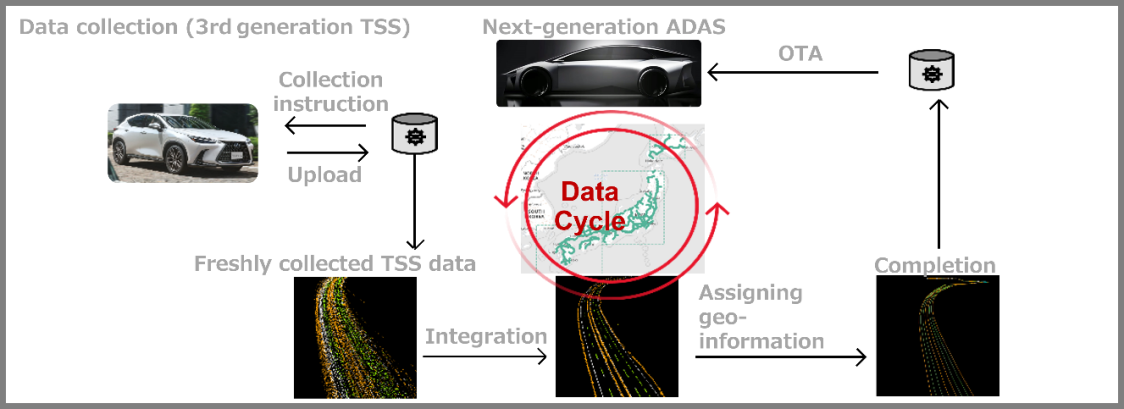
Automatic map generation (Geo)
- The resolution of road gradient information is dramatically improved through Toyota’s vast amount of vehicle data an in increase in the frequency of 3D map updates from six months to same-day.
- This enables comfortable, safer and more fuel/electricity-efficient driving.
New, next generation automatic parking
- This provides “smart parking” in various locations, based on registered parking patterns. The system can respond to irregular situations such as obstacles, using autonomous driving technology.
Toyota e-Palette
- Two types of the Toyota e-Palette are available for diverse applications: one without a driver’s seat (automatic operation) and one with (with manual operation possible). The interior space can be use to provide different services, for example a mobile convenience shop.
- The vehicle uses an autonomous driving system being developed by Toyota, Woven by Toyota and Denso. It contributes to the aim of “mobility for all,” using autonomous driving capability that only a carmaker can provide, based on intelligence gained from extensive data and safety knowledge accumulated over many years.

DIVERSIFICATION TECHNOLOGY
Greater comfort and free mobility are important elements in the way people’s live can be enriched by cars. Toyota is a global operation and knows how customer values differ from region to region and generation to generation. To meet these expectations, it seeks to offer diverse products and services.
As an example, it has developed a one-touch wheelchair fastening device for vehicles, using know-how gained from developing vehicles that can accommodate disabled people over many years (known as “welfare vehicles” in Japan).
The company is working to diversify mobility with the JUU electric wheelchairs, which makes getting in and out of a vehicle less stressful and allows the chair to be used on uneven surfaces, including stairs. This expansion of wheelchair functions offers greater freedom of mobility.
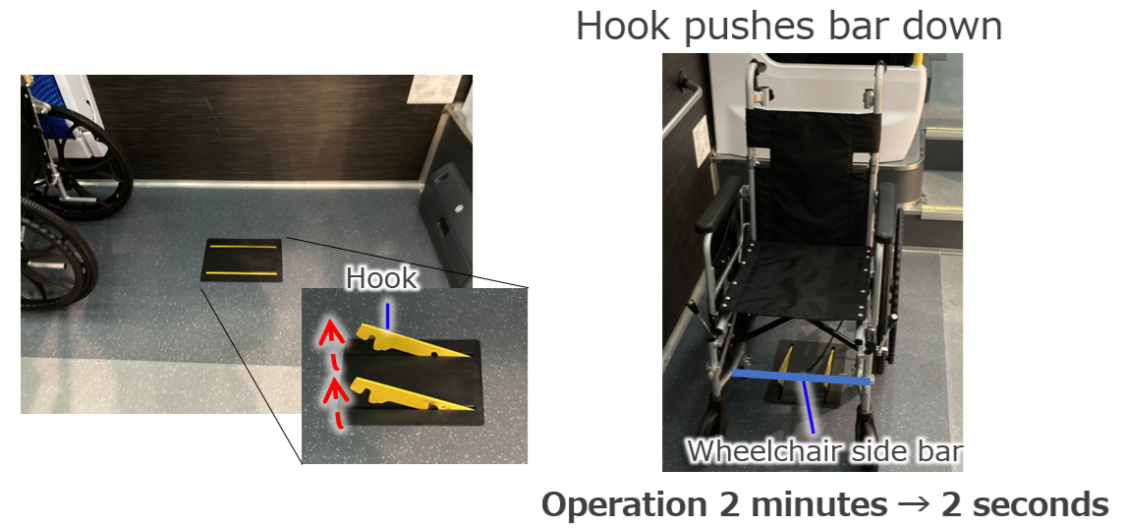
One-touch wheelchair fasting device
- Toyota has developed a system anyone can use to easily and firmly secure a wheelchair to a vehicle.
- The widespread use of this technology could open greater freedom of travel. For example, the wheelchair users could travel in their own car to a bus stop, transfer to an airport bus and then fly to their destination. Once there, they could have similarly stress-free travel in cabs or boats.
- To help make this happen, the automobile and wheelchair industries are working together to create standards. In the future, these standards will be expanded not only to automobiles, but to land, sea, air and other forms of mobility to realise even greater freedom of movement.
JUU electric wheelchair
- Mobility device that can go up and down stairs, contributing to barrier-free access.
- It can climb 160mm steps and be used on uneven roads/surfaces.
- The driver motor uses electric power steering for high torque and safety.

ENDS

