Toyota Yaris Takes The Lead In Passive Safety Once Again
ADAC Tests Confirm Yaris Seats Provide The Best Whiplash Protection
The German autoclub ADAC recently tested the seats of several city cars in terms of the protection they offer in the event of a rear crash. In spite of competing against more recent models, the Toyota Yaris registered the best performance.
Although whiplash injury protection is not regulated by European standards or safety organisations, injuries caused by rear impacts can prove to be more serious than one might think. In fact, the main danger suffered during these kinds of accidents is the ‘whiplash’ effect. When a car is hit from behind, the occupants’ heads will tend to roll backwards, which exerts an enormous stress on the neck. In extreme situations this may even result in a fatal injury to the passenger. Even a 6mph rear impact can sometimes bring permanent neck injuries to occupants, which is not only painful but also expensive to treat.
The 2003 ADAC crash tests heighten awareness of this important area of passive safety which has been comparatively overlooked in the past. ADAC chose to test 10 different city cars in order to judge how well some of the most affordable cars in the market comply in terms of whiplash protection.
The performance of the 10 contenders’ seats was judged in two different areas. First, the seat must be able to provide adequate protection against whiplash-effect injuries; second, it must have a rigid structure in order to provide stable support for the passenger’s body. Final results point Yaris’s seats as equal best with the smart. Other contenders included the Renault Clio, MINI and Nissan Micra
WIL Seats, a Toyota Engineering Achievement
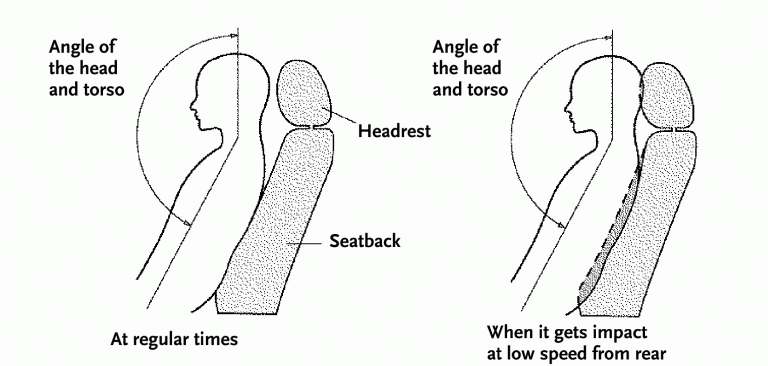
The Toyota Yaris is equipped with WIL (Whiplash Injury Lessening) seats. The WIL concept is applied in order to reduce the risk of whiplash injuries in the sequence of a rear impact.
The system’s efficiency (proven by the ADAC test) is matched only by its simplicity and ingenuity. WIL seats are equipped with a special seatback structure that works in tandem with the headrest to provide the passenger’s body with the right posture.
In the event of a rear crash, the seat will allow the lower part of the body to be pulled back. At the same time the seatback and the headrest will be closer to the upper torso, neck and head, providing full support and preventing the head’s natural rotation.
The simplicity of this system makes it possible for Toyota to install it throughout the passenger car range as standard equipment with low impact in terms of cost. The first WIL seats were installed in the Toyota Prius in 1997
ENDS