Toyota’s ‘Mild Hybrid’ Boosts Fuel Efficiency 15 Per Cent
Toyota have unveiled a simple, easy-to-adapt hybrid system called Toyota Hybrid System-Mild (THS-M) that is ideal for application in many types of cars. Toyota plans to introduce this fuel-saving, emissions-reducing system in actual production vehicles in Japan later this year.
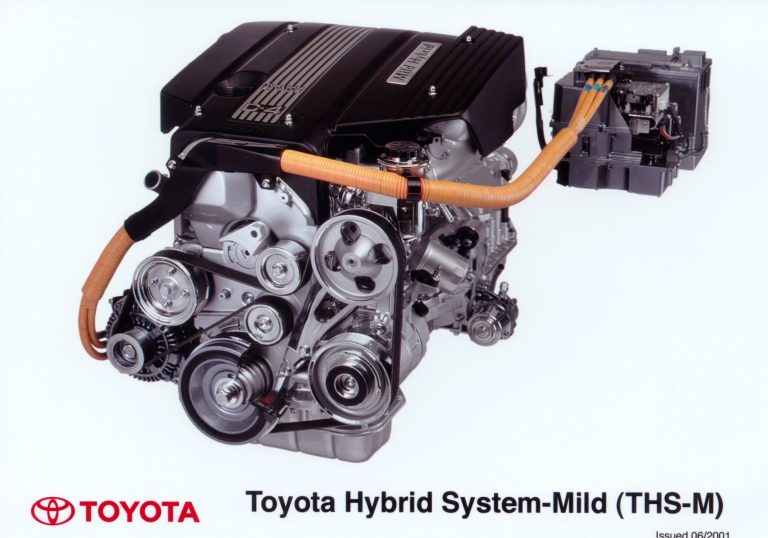
THS-M comprises of three main components; a small motor/generator connected via a belt to a high-efficiency petrol engine, a compact 36V secondary battery for appropriate power supply to the motor and a control unit.
When a vehicle equipped with THS-M comes to a stop, the system goes into “idling stop” mode, automatically shutting down the petrol engine to prevent idling. To get the vehicle moving again, the electric motor provides the initial drive force and restarts the petrol engine. When decelerating or braking, the motor acts as a generator to convert braking energy into electrical energy that is recovered by the battery. The motor also enables the air conditioning to run during “idling stop” to help occupants stay comfortable.
THS-M improves fuel efficiency by about 15 per cent (in the Japanese test cycle for vehicles with automatic transmissions) and reduces emissions. When combined with a direct fuel-injection petrol engine, a 50 per cent lower level should be attainable than those set for 2000 by the Japanese government. Toyota plans to release the first THS-M vehicle in Japan this autumn. That car will feature a 6 cylinder, 3.0-litre engine and three-phase AC synchronous electric motor.
The system’s 36V battery (in a 42V power system) suitably meets the large electrical power needs of hybrid vehicles and appropriately handles the increasing electrical load of modern cars. The higher voltage and resulting smaller possible current in a 36V battery system allow wire harnesses to be much thinner than those used in standard 12V systems, contributing to overall weight reduction and resource conservation. Moves are planned towards the international standardisation of the 36V battery as the next-generation electrical power source (42V Power system) for cars.
THS-M is the latest in a number of Toyota advances in the practical application of environment-friendly automotive technology. In 1997, Toyota introduced the Prius, the world’s first production hybrid vehicle. Featuring THS (Toyota Hybrid System), this family saloon is powered by an electric motor and petrol engine and has recently surpassed the 50,000 mark in Japanese sales, with total sales worldwide of around 60,000 units. Toyota will very soon increase its hybrid line up with a Previa MPV based car featuring THS-C (Toyota Hybrid System-CVT), which provides drive power suited to larger vehicles. Toyota is also applying its hybrid know-how to fuel cell-powered vehicles, such as in the development of a fuel cell hybrid vehicle, or FCHV.
System Overview
Instead of the belt-driven alternator (generator) used in conventional engines,
THS-M uses a motor/generator (MG). Powered by a 36V battery, the motor/generator acts as either a motor or generator, switching between functions according to driving conditions.
The motor/generator has the following functions:
- Restarts engine from “idling stop” mode.
- Starts vehicle moving before engine kicks in after “idling stop” mode.
- Charges battery (as needed) during engine operation.
- Regenerates energy during vehicle deceleration and braking.
- Powers accessories such as air conditioner compressor when in “idling stop” mode.
Features
- The “idling stop” mode and energy regeneration while decelerating or braking give lower fuel consumption and emissions; at the same time, idling noise is reduced.
- The combination of a belt-driven motor/generator and a 36V compact battery enables smooth, natural engine starts and acceleration from rest. THS-M’s simple design means it can easily be used in existing vehicle models.
- THS-M allows the air conditioning to run even during “idling stop”.
THS-M operation according to situation
|
Driving state |
Function |
|
While stopped |
When the vehicle stops, the system shuts down the engine. The electromagnetic clutch is turned off and the MG powers accessories. This allows the air conditioner to run while in “idling stop” mode for increased comfort. |
|
Accelerating from rest |
When accelerating from rest, the 36V battery powers the MG, which drives the vehicle and restarts the engine. (The starter is used for initial engine ignition.) |
|
Cruising |
The engine drives the vehicle. When the battery’s SOC (State of Charge) is low, the MG switches to generator mode to charge the battery. |
|
During deceleration |
When decelerating or braking, the wheels drive the MG in a regeneration process that charges the battery. This means that part of the vehicle’s running loss energy is recovered by the battery. |
ENDS